| Our laboratory focuses on the research that handles hydrogen isotopes including
tritium which is fuel of a fusion reactor.We aim to understand elemental
phenomena that are required to develop fusion reactor, fission reactor
and next-generation energy system utilizing hydrogen, and to optimize these
systems as an aggregate of elements. Scientific education and research
about experiment and numerical analysis are conducted from the viewpoint
of process engineering. |
 |
|
 |
Tritium experimental room
A lot of findings have been obtained through the tritium experiment.Recently,
we are working on the quantitative understanding of the tritium behavior
in concrete materials and plasma facing materials, in addition to tritium
breeding materials.
|
 |

|
 |
 |
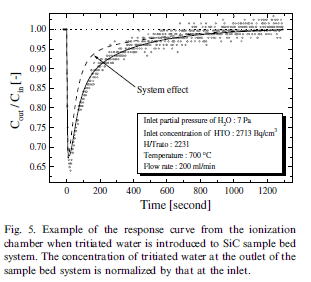
| Tritium trapping on the surface of SiC |
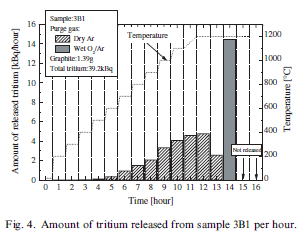
Release of tritium impranted into JT60 graphite tile |
|
 |
|
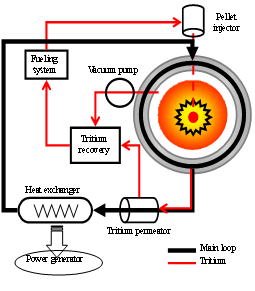
Study on behavior of hydrogen isotopes in liquid blanket.
The
blanket in a fusion reactor plays very important roles, (i) tritium breeding
for fuels supply, (ii) heat exchange for energy, (iii) shielding radiation for
safety. Liquid blanket system has some advantages such as simple blanket
structure, a high tritium-breeding ratio, a high thermal conductivity.
Candidate materials of liquid blankets are Li, Li17Pb83,
FLiBe, and so on. We study about the behavior of hydrogen isotopes in their
material, especially Li and Li17Pb83 in order to
construct a reliable tritium recovery system with low tritium leakage. The use
of Li is expected for a flowing target in the International Fusion Materials
Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) for high-intensity
neutron generation. IFMIF is designed to test materials durability under high
intensity neutron-irradiation conditions of the future commercial fusion
reactors. Our research group has been developed a Y hot trap
for remove tritium from Li loop. Li17Pb83 is one of the most
promising candidate materials for liquid blankets in fusion reactors. We are studying
about tritium behavior in Li-Pb blanket for design the tritium recovery system.
|
 |
|
 |
Study on tritium behavior in solid breeder materials.
under construction. |
|
 |
Study on tritium behavior in re-deposited layer
The plasma facing wall is eroded by interaction with high-energy particles
and impure particles are emitted to the plasma. A part of the emitted impurities
returns to the surface of the wall via some interactions with the plasma
and it forms a re-deposition layer or dust containing fuel atoms. From D-T experiments such as Joint
European Torus (JET) or Tokamak Fusion Test Reactor (TFTR), it has been
revealed that a large amount hydrogen isotope is retained in carbon-based
co-deposition. From the viewpoint of fuel recycling and
assurance of tritium safety, it is essential to understand the sorption and
desorption behavior of tritium from not only plasma facing materials but also
re-formed materials. However, discussions about tritium behavior
in tungsten a re-deposition layer have not been performed sufficiently. In this study, we made various re-deposited layers by a sputtering method using hydrogen RF plasma. The amount of hydrogen isotopes trapped in the layer is quantified. |
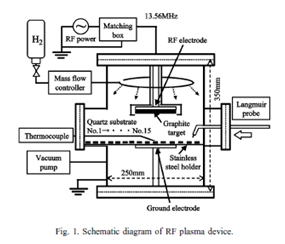 |
 |
|
 |
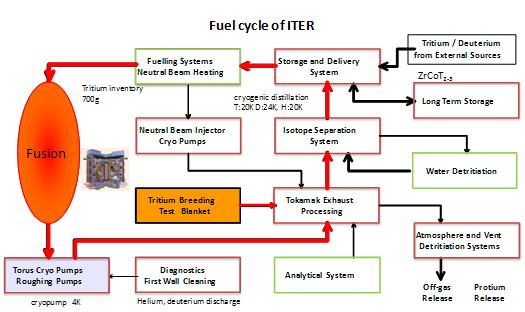
Study on desorption of hydrogen, helium and methane from cryo-sorption
pump
A key issue to establish the tritium (T) fuel cycle of fusion reactor systems
such as DEMO or the future commercial reactors is to reduce tritium inventory
for increasing potential safety of D-T fusion reactors. In order to do
that it is necessary to constitute a self-sufficient reactor system.The
first process of the fuel cycle after D-T burning is the evacuation of
gas mixtures including hydrogen isotopes, helium and impurities by cryo-sorption
pumps or turbo molecular pumps.The cryo-sorption pump has be used for the
evacuation system for the reasons that high magnetism tolerance and high
vacuum speed of all gases. However, the process of regeneration to discharge
the gases saved up is needed for cryo-sorption pump because that is a pump
of the saving up type. Therefore, it is necessary to examine several gas
discharge behavior from the cryo-sorption pump under various conditions. |
|
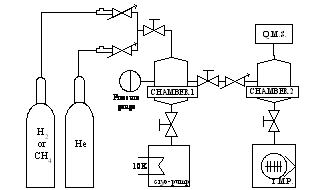 |
|
|








